Induction motors are widely used in industries to meet various requirement. This can be realized by that fact that, around 90% motors used in industries are Induction motors. The motors plays an important role in the plant process and failure or outage of motor may lead to loss in production or may even hamper the plant safety system. Therefore, it becomes very important to implement proper motor protection scheme.
Based on the process application of motors, different protection schemes are used. Motor Protection philosophy for HT and LT motor are almost same with some difference. In some HT motors, some additional protection may also be provided like Differential Protection. However, the motor protection for HT and LT motors are almost same. But their method of implementation are different.
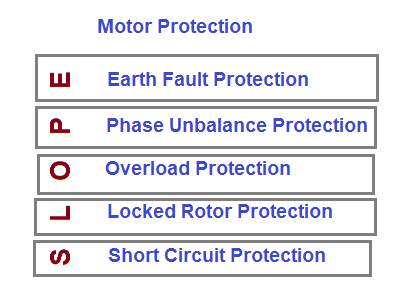
The common motor protection provided for HT and LT motors are:
- Short Circuit Protection (50)
- Locked Rotor Protection or Blocked Rotor Protection (14)
- Over Load Protection (49)
- Phase Unbalance Protection (46)
- Earth Fault Protection (50N)
These protections can easily be remembered using word “SLOPE”. The description of this “SLOPE” is shown below:
The above five protection schemes for HT motors i.e. 6.6 kV motors are implemented using CTMM or Numerical Relays. These days, numerical relays are preferred over CTMM relays due to various advantages offered by Numerical Relays. However, in LT motors, above five protections are used differently. In some cases where the kW rating of LT motor is more (generally more than 75 kW), CTMM or Numerical Relays are used. In the numerical relay, setting for the five protection are incorporated and, then tested to ensure that setting is meeting the protection intent.
However, for small sized LT motors (generally less than 75 kW), Fuse and Motor protection relay (like L&T Make MN relay in conjunction with contactor) are used. Fuse provides protection against the short circuit. MN Relays provide protection for thermal overload and erath fault is provided by using some different relay protection.
GOOD INFORMATION OF HV MOTOR PROTECTION.
THANKS
KINDLY SEND ME GENERATOR PROTECTION IN EASY WAY