In Sulpher Hexafluoride or SF6 Circuit Breaker, sulpher hexafluoride (SF6) gas is used as an insulating and arc quenching medium. SF6 gas has many superior properties which makes it perfect for arc quenching.Sulpher Hexafluoride or SF6 Circuit Breaker is most popular and widely used breaker. This type of breaker is mostly used for EHV systems like 220 kV, 400 kV and 765 kV. It is suggested to read “Why SF6 gas used in HV/EHV Circuit Breakers“.
Construction of SF6 Circuit Breaker
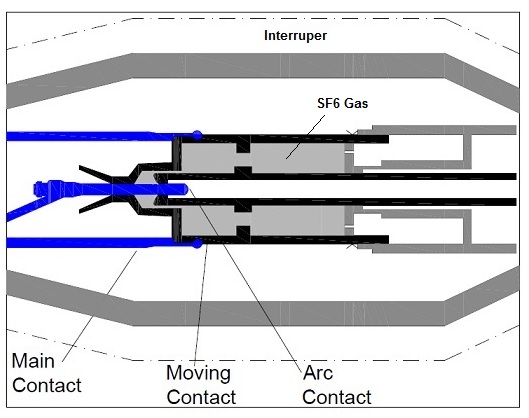
Like other circuit breaker viz. Vacuum Circuit Breaker, Air Blast Circuit Breaker etc., SF6 Circuit Breaker has fixed contact as well as moving contact. Theses fixed and moving contacts are known as MAIN CONTACT. There exists one another contact which is known as ARCING CONTACT. Arcing Contact is part of fixed contact. Basically, Arcing contacts are only designed to withstand arcing. It is not designed for carrying load current. In spite, main contacts are designed to carry load current and not the arcing.
Therefore, it can be said that, while closing of SF6 circuit breaker, first Arcing Contact will close. Thereafter arcing contact will close. Similarly while opening, first main contact will open and then arcing contact will open. Notice here that, during opening operation of SF6 Circuit Breaker, the order of opening main and arcing contact is revered as that in closing operation. This is because, while opening if the main contact opens first, there will not be any arcing as the current is getting path through the arcing contact. But if the arcing contact open first then during opening of main contact there will be arcing and as discussed main contacts are not meant to withstand arcing.
Apart from Fixed contact and moving contacts, SF6 Circuit Breaker has following main components:
- Interrupter
- Insulating Nozzle
- SF6 Gas Chamber
An interrupt is a chamber which encloses the breaker contacts, insulating nozzle, SF6 gas chamber. Interrupter is made of porcelain. Figure below shows the basic parts of SF6 circuit breaker.
Carefully observe the figure and notice the different parts, though some parts like SF6 gas chamber, nozzle, valve etc are not shown in the above figure but they will be shown while discussing the working principle. So, please be patient till then and read further.
Working Principle of SF6 Circuit Breaker
The contacts of SF6 Circuit Breaker are surrounded in an environment of SF6 gas at some pressure. Actually, the dielectric strength of SF6 gas is directly proportional to its pressure. In 220 kV, 400 kV and 765 kV applications, the gas pressure is maintained at 6.5 bar. Let’s consider breaker opening operation for better understanding of operating mechanism. First have a look at the contacts when the breaker is in fully close position as shown in Figure-1.
Now we will open the breaker and will observe its mechanism step by step.
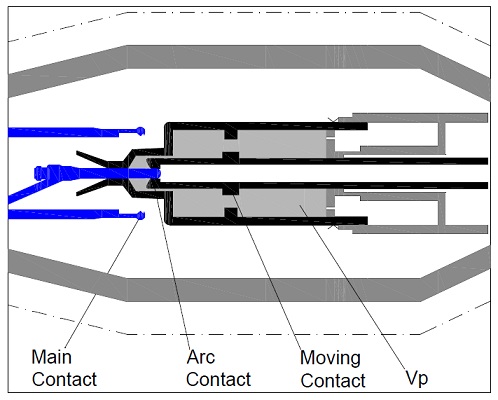
Step-1: Main Contact Open
As discussed earlier in the post, main contact will open first. This is shown in the figure above. Observe in figure that, though main contacts are open, arcing contacts are still close. As main contacts open, the piston in the cylinder moves causes the SF6 gas to compress due to reduction of volume Vp.
Step-2: Arcing Contacts Open
As soon as arcing contacts separates from contact 1, an arc is strikes. Due to this arcing, heat is produced. This heat of arc further increases the pressure of SF6 in the chamber Vt. Mind that, the pressure of arc extinguisher i.e. SF6 is increased by the heat of arc. This is the reason; such breaker is called self compensating type. Here self compensating means that, the capacity of breaker to interrupt the fault is proportional to fault current.
Step-3: Arcing Contact separates from Nozzle
When arcing contact separates from the insulating Nozzle, the pressurized SF6 gas in volume Vt is released in the arc. This causes the arc to extinguish at the moment the current passes though the natural zero. Thus, the pressurized SF6 gas extinguishes the arc and hence circuit is interrupted.
In case of small current like in unloaded transformer or reactor, the thermal energy of arc is not enough to pressurize the SF6 gas. In such case the pressure developed in the SF6 gas chamber Vp in Step-1 is extinguishes the arc.
Types of SF6 Circuit Breaker
As discussed, in 220 kV, 400 kV and 765 kV applications, the SF6 gas pressure is maintained at 6.5 bar. You will be amazed that, even though voltage level is increasing, same pressure of SF6 i.e. 6.5 bar is used for 220, 400 and 765 kV applications. Actually as we go up at higher voltage level, the number of contacts increases in SF6 circuit Breaker. Based on this philosophy, SF6 circuit breaker can be classified into following types:
- Single Breaker Circuit Breaker
- Double Break Circuit Breaker
- Multi Break Circuit Breaker
Single Break SF6 Circuit Breaker
In Single Break Circuit Breaker, only one moving and fixed contacts are present. This means that, there will only be one interrupter unit in such breaker. Single break SF6 circuit breaker is used for 220 kV applications.
Double Break SF6 Circuit Breaker
In such type of breaker, there are two set of moving and fixed contacts connected in series. Therefore, to enclose two set of contacts, there must be two interrupt unit in series. This type of breaker is used in 400 kV applications. In double break circuit breaker, grading capacitors are used to equalize the voltage distribution across each contact. Thus for 400 kV application, the voltage across each contact will be 200 kV. Therefore it is logical to use SF6 gas at a pressure same as used in 200 kV application. Ha ha..got it?
Multi Break SF6 Circuit Breaker
In multi break circuit break, more than two set of fixed and moving contacts are used. Such type of breaker is used in 765 kV applications.