Induction Motor works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The three phase input power supplied to stator terminal is converted into mechanical power at the shaft output. This conversion of energy takes place through magnetic coupling between stator produced rotating magnetic flux and rotor bars. The power transfer from stator to rotor takes place through the air gap. The power available at the air gap of induction motor is called Air Gap Power. It is denoted as Pg.
Air Gap Power is basically the rotor input power. It is the gross power available at rotor input and supplies ohmic loss, friction & windage loss and mechanical power output. Therefore,
Mechanical Power Output Pm = Pg – Rotor Ohmic Loss – Friction & Windage Losses
Calculation of Air Gap Power
Let us consider the equivalent circuit of rotor circuit of induction motor as shown in figure below:
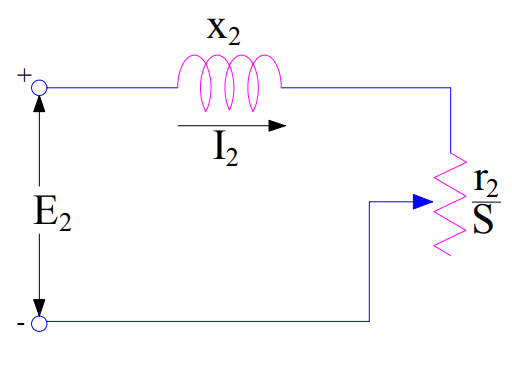
In the above figure, x2, r2/s and E2 are the rotor leakage reactance and rotor winding resistance and per phase generated Rotor terminal EMF at power frequency. If you find any difficulty in understanding this equivalent circuit, please read Induction Motor Phasor Diagram.
From the above equivalent circuit, per phase power input to the rotor is give as
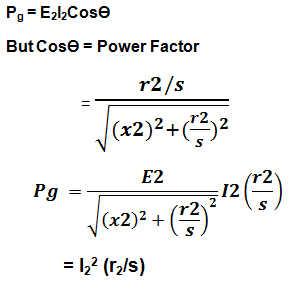
From the above expression, it is clear that per phase rotor power input is equal to I22(r2/s) as reactance x2 do not consume any power. Pg is the power transferred from stator to the rotor across the air gap. Therefore it is called the Air Gap Power.
This air gap power is converted into mechanical power output at shaft and losses viz. frictional and windage loss.
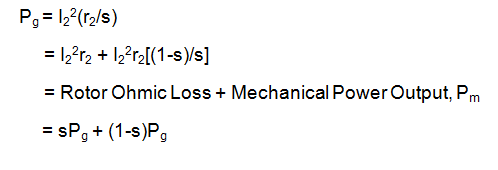
Thus, rotor ohmic loss and mechanical power output in Induction Motor are given as
Pm = (1-s)Pg
Rotor Ohmic Loss = sPg
This mechanical power output accounts the shaft power and friction & windage loss. Therefore,
Shaft Power Psh = Pm – Friction & Windage Losses
Thus stator supplied power is converted into air gap power. This air gap power is then converted into mechanical power. Mechanical power is finally transferred to shaft output of induction motor.